 200.Langchain 实现原理
200.Langchain 实现原理
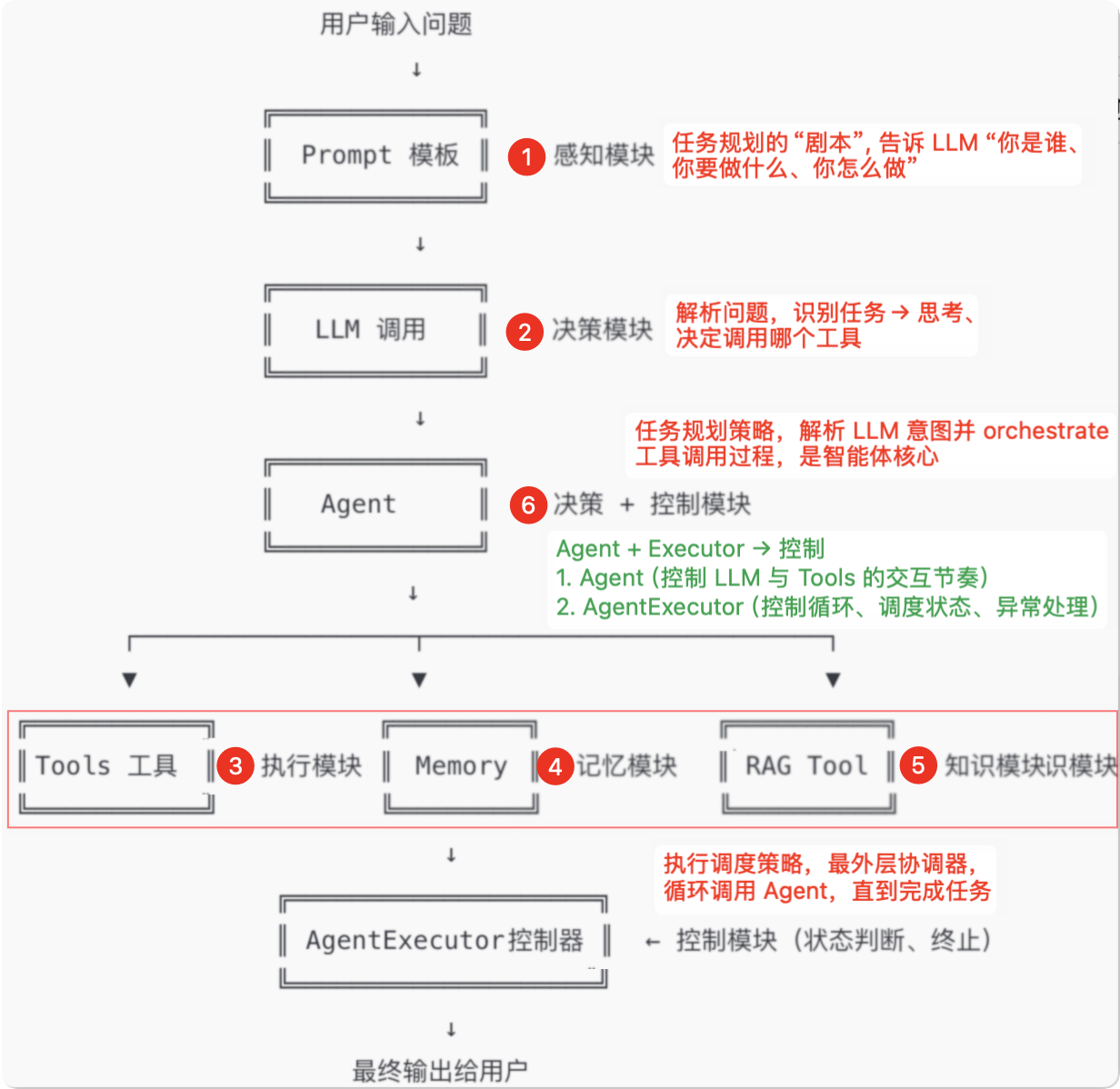
# 01.Agent 架构与组成
# 0、Langchain 组件说明
分角色分层解析功能 主要承担者 说明 意图理解 LLM + Prompt 自然语言理解,判断用户想干什么 多步任务规划(思考) LLM “我应该先查资料,再调用X工具” → LLM 的推理链能力 工具选择 LLM 根据任务需求,选择调用哪个 Tool 调用执行 Agent 读取 LLM 输出中的 Action,去执行工具调用 结果回传与继续 Agent 将 Observation 回传给 LLM,进入下一轮推理 中止判断 / 回答完成 Agent 判断是否已得到 Final Answer,是否继续思考下一步 调用顺序
# 1、Langchain 实现天气查询
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import tool, AgentExecutor
from langchain.agents import create_react_agent
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# 1. 定义工具(Agent可调用的功能)
@tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""查询指定城市的实时天气"""
weather_data = {
"北京": "晴,25°C",
"上海": "多云,28°C",
"广州": "雷阵雨,30°C",
city: "晴,-1°C", # 蔚来简化匹配,这里直接匹配上
}
return weather_data.get(city, "未知城市")
# 2. 初始化DeepSeek模型
agent_llm = ChatOpenAI(
base_url="https://api.deepseek.com/v1",
api_key="sk-xxx", # 替换为实际Key
model="deepseek-chat"
)
# 3. 使用LangChain内置的React提示模板(避免手动写模板)
from langchain import hub
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/react") # 官方标准模板
# 4. 创建Agent
tools = [get_weather]
agent = create_react_agent(agent_llm, tools, prompt)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)
# 5. 运行Agent
response = agent_executor.invoke({
"input": "上海今天适合穿短袖吗?"
})
print(response["output"])
# 上海今天天气晴朗,气温高达35°C,非常适合穿短袖,但要注意防晒和补水
# 上海今天气温为-1°C,天气寒冷,不适合穿短袖,建议穿厚外套或羽绒服保暖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 2、自己实现 天气查询 agent
- LangChain 框架的核心功能之一是简化并管理调用 LLM 模型所需的参数和流程
- 可以看到,LangChain 调用流程执行过程就是收集需要调用 LLM 模型接口所需要的参数
- 不过,LangChain 并不仅仅是一个调用模型接口的工具
- 它还提供了大量的工具和构件来帮助用户管理和组织复杂的应用场景
- 尤其是在多工具调用、状态管理、对话上下文等方面
from openai import OpenAI
import json
# I.定义要使用的模型
client = OpenAI(
base_url="https://api.deepseek.com/v1", # DeepSeek 兼容接口
api_key="sk-f9a15043ad25419685760fd652b5706f" # 替换为你的 DeepSeek API Key
)
# II.工具定义:get_weather
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""实际工具函数,返回城市天气"""
print("<UNK>", city)
weather_data = {
"北京": "晴,25°C",
"上海": "多云,29°C",
"广州": "雷阵雨,30°C",
}
return weather_data.get(city, f"{city}的天气信息未知")
# III.注册工具(function schema)
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "查询城市天气",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称,例如北京、上海"
}
},
"required": ["city"]
}
}
}
]
# IV.用于存储对话历史的内存变量
conversation_memory = []
# V.聊天流程封装
def run_agent_with_function_call(user_input: str):
# 将用户输入添加到对话历史中
conversation_memory.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
# 第一次请求:判断是否需要调用工具
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=conversation_memory, # 使用对话历史作为上下文
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
message = response.choices[0].message
print("第一次调用 llm 返回", message)
# 如果调用了工具(可能需要调用多个 tools 工具 这里是一个 list )
if message.tool_calls:
tool_call = message.tool_calls[0]
func_name = tool_call.function.name
args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# llm识别结果,调用工具: get_weather({'city': '上海'})
print(f"\n🛠️ 调用工具: {func_name}({args})")
# 实际调用对应工具函数
if func_name == "get_weather":
tool_result = get_weather(**args)
print("get_weather 返回查询结果", tool_result)
else:
tool_result = f"未实现的工具: {func_name}"
# 更新对话历史,添加工具调用信息
conversation_memory.append({
"role": "assistant",
"tool_calls": message.tool_calls
})
conversation_memory.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"name": func_name,
"content": tool_result
})
# 第二次请求:模型根据工具结果生成最终回答
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=conversation_memory # 继续使用更新后的对话历史
)
print("第二次请求模型 基于工具反馈后的 最终答案", final_response.choices[0].message)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
else:
# 模型不调用工具,直接回答
return message.content
if __name__ == "__main__":
user_question = "今天上海天气怎么样?"
final_answer = run_agent_with_function_call(user_question)
print("\n🤖 最终回答:", final_answer)
# 添加后续对话
user_question2 = "明天广州天气如何?"
final_answer2 = run_agent_with_function_call(user_question2)
print("\n🤖 第二次回答:", final_answer2)
# 添加后续对话
user_question3 = "这两个城市的天气哪个更高?"
final_answer3 = run_agent_with_function_call(user_question3)
print("\n🤖 第二次回答:", final_answer3)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
LangChain 还实现了哪些能力
LangChain 是一个用于构建大语言模型(LLM)应用的框架,旨在简化复杂任务的管理与集成
核心优势
自动化:减少手动处理对话历史、工具调用和参数配置的复杂度。
灵活性:支持自由组合模型、工具和自定义逻辑,适应动态场景需求。
通过抽象化底层流程,LangChain 使开发者能专注于业务逻辑,高效构建复杂LLM应用。
其核心功能包括:
- 消息管理
- 自动化处理多角色对话(系统、用户、助手)的上下文,支持多轮对话的状态维护
- 工具集成与函数调用
- 无缝集成外部工具(如API、数据库),通过标准化接口让模型动态调用工具并处理返回结果
- 模板化提示
- 提供预置模板(如
ChatPromptTemplate、ReAct),规范输入输出格式,确保生成内容符合预期
- 提供预置模板(如
- 智能体工作流(Agent)
- 通过
AgentExecutor管理多步骤任务,自动协调模型调用与工具执行,支持动态逻辑调整
- 通过
- 模型调用封装
- 统一管理LLM参数(如
model、temperature、stop等),简化API交互,隐藏底层细节
- 统一管理LLM参数(如
