 02.Spring之AOP
02.Spring之AOP
# 01.Spring之AOP
# 1、AOP概述
代理(Proxy)- SpringAOP的核心本质是采用代理模式实现的
连接点(JoinPoint)- 在SpringAOP中,理解为任意方法的执行
切入点(Pointcut)- 匹配连接点的式子,也是具有共性功能的方法描述
- 例如:update()、delete()方法,select()方法没有被增强所以不是切入点
通知(Advice)- 在
切入点前后执行的操作,也就是增强的共性功能 - 在SpringAOP中,功能
最终以方法的形式呈现 - 包括了“around”、“before”和“after”等不同类型的通知(advice)
- 在
通知类- 通知方法所在的类叫做通知类
切面(Aspect)- 描述通知与切入点的对应关系,也就是
哪些通知方法对应哪些切入点方法
- 描述通知与切入点的对应关系,也就是
目标对象(Target)- 被代理的原始对象成为目标对象
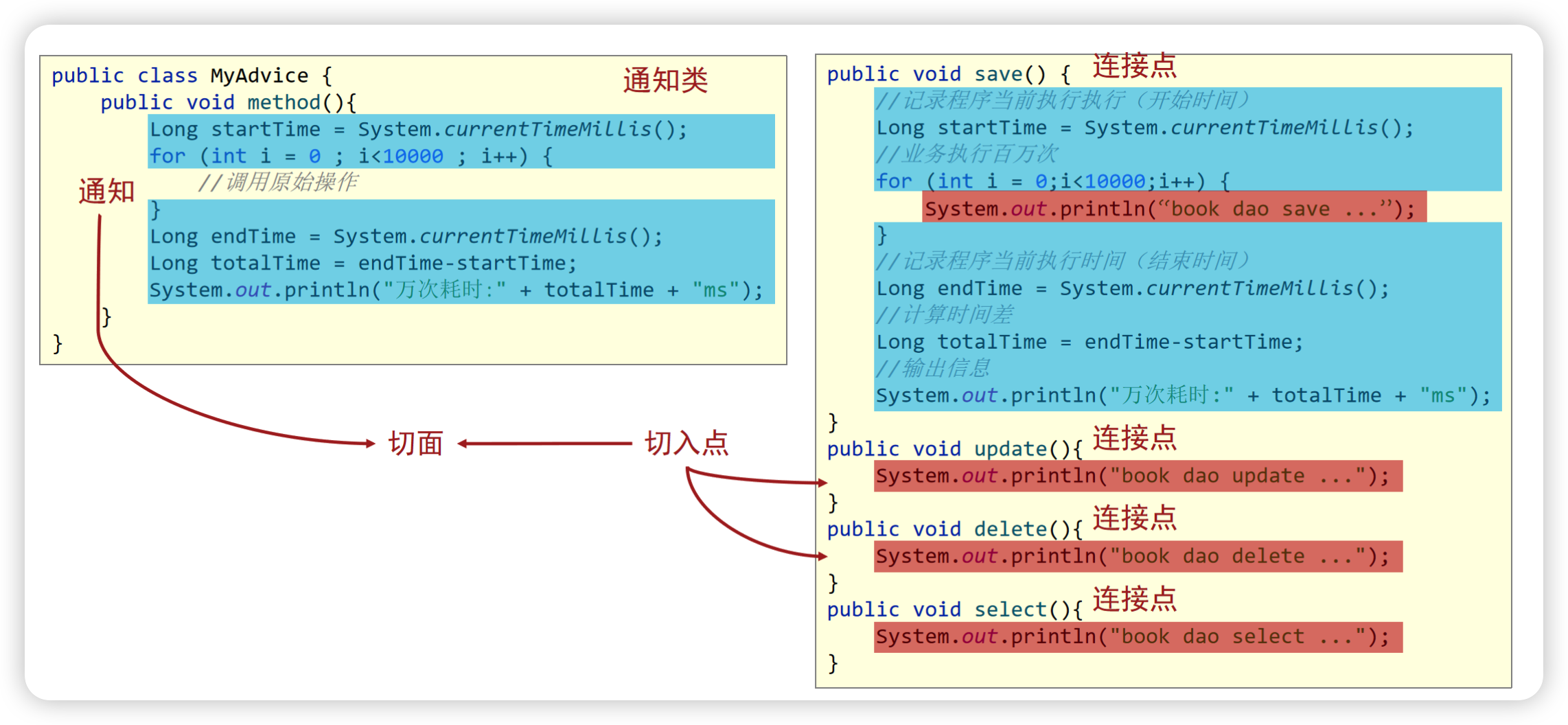
# 2、AOP案例
- 当匹配到规则的连接点回执行方法,没有匹配的不执行
spring03_aop
├── pom.xml
├── src
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── java
│ │ │ ├── App.java
│ │ │ └── org
│ │ │ └── example
│ │ │ ├── aop // 切面相关的包
│ │ │ │ └── MyAdvice.java // 定义了一个切面,用于在BookDao的update方法执行前打印一条日志
│ │ │ ├── config
│ │ │ │ └── SpringConfig.java
│ │ │ └── dao
│ │ │ ├── BookDao.java
│ │ │ └── impl
│ │ │ └── BookDaoImpl.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1)pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2)aop/MyAdvice.java
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//指定这个类是一个Spring的组件,Spring会自动扫描和管理这个类的实例
@Component
//Spring AOP的注解,表示这个类是一个切面,用于定义一些针对多个类或者方法的通用行为
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
//Pointcut定义了一个切入点,表示这个切面会影响哪些类或者方法
@Pointcut("execution(void org.example.dao.BookDao.update())")
//pt()是切入点的具体方法,但在这里并无实际执行的功能,只是作为一个标记,供@Before("pt()")使用
private void pt(){}
//通知(Advice)的注解,表示在切入点方法执行前,要执行的一段代码
@Before("pt()")
public void method(){
System.out.println("执行 MyAdvice.pt() 方法");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
3)dao
// dao/BookDao.java
public interface BookDao {
public void save();
public void update();
}
// dao/impl/BookDaoImpl.java
import org.example.dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("book dao save ...");
}
public void update(){
System.out.println("book dao update ...");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
4)config
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfig {
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
5)App.java
import org.example.config.SpringConfig;
import org.example.dao.BookDao;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);
bookDao.update();
// bookDao.save();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 3、切入点表达式语法
//1)精确匹配:只有指定这个类中返回类型为void且没有参数的`update`方法
@Pointcut("execution(void com.itheima.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update())")
//2)匹配:只有指定这个类中返回类型为void且有且只有一个参数的`update`方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl.update(*))")
//3)匹配`com`包及其子包下的类中返回类型为void且没有参数的`update`方法
@Pointcut("execution(void com.*.*.*.update())")
//4)应用于任意包下的类中的任意方法
@Pointcut("execution(* *..*(..))")
//5)应用于任意包下的类中方法名以`e`结尾的方法
@Pointcut("execution(* *..*e(..))")
//6)应用于`com`包及其子包下的类中返回类型为void且没有参数的任意方法
@Pointcut("execution(void com..*())")
//7)应用于`com.itheima`包下类名以`Service`结尾且方法名以`find`开头的方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.*.*Service.find*(..))")
//8)应用于`com.itheima`包下类名以`Service`结尾且方法名为`save`的方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.itheima.*.*Service.save(..))")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 4、五种通知Advice
@Before- 前置通知,表示在目标方法执行前,会先执行通知方法
- 例如,可以在调用一个保存数据的方法前,先执行一个检查权限的方法
@After- 后置通知,表示在目标方法执行后,无论目标方法是否发生异常,都会执行通知方法
- 例如,可以在调用一个修改数据的方法后,执行一个记录日志的方法
@AfterReturning- 返回后通知,表示在目标方法成功执行后,会执行通知方法
- 例如,可以在调用一个查询数据的方法后,执行一个对查询结果进行处理的方法
@AfterThrowing- 异常通知,表示在目标方法抛出异常后,会执行通知方法
- 例如,可以在调用一个更新数据的方法抛出异常后,执行一个进行错误处理的方法
@Around- 环绕通知,表示在目标方法执行前后,都会执行通知方法
- 这是最强大的一种通知类型,可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为
- 例如
- 可以在调用一个处理数据的方法前,执行一个开始计时的方法
- 然后在方法调用后,执行一个结束计时的方法,以此来测量方法的执行时间
# 02.事务案例
# 1、创建表
create database if not exists spring_db character set utf8;
use spring_db;
create table if not exists tbl_account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
money double
);
insert into tbl_account values(null,'Tom',1000);
insert into tbl_account values(null,'Jerry',1000);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
USE spring_db;
CREATE TABLE tbl_log(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
info VARCHAR(255),
createDate DATE
);
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
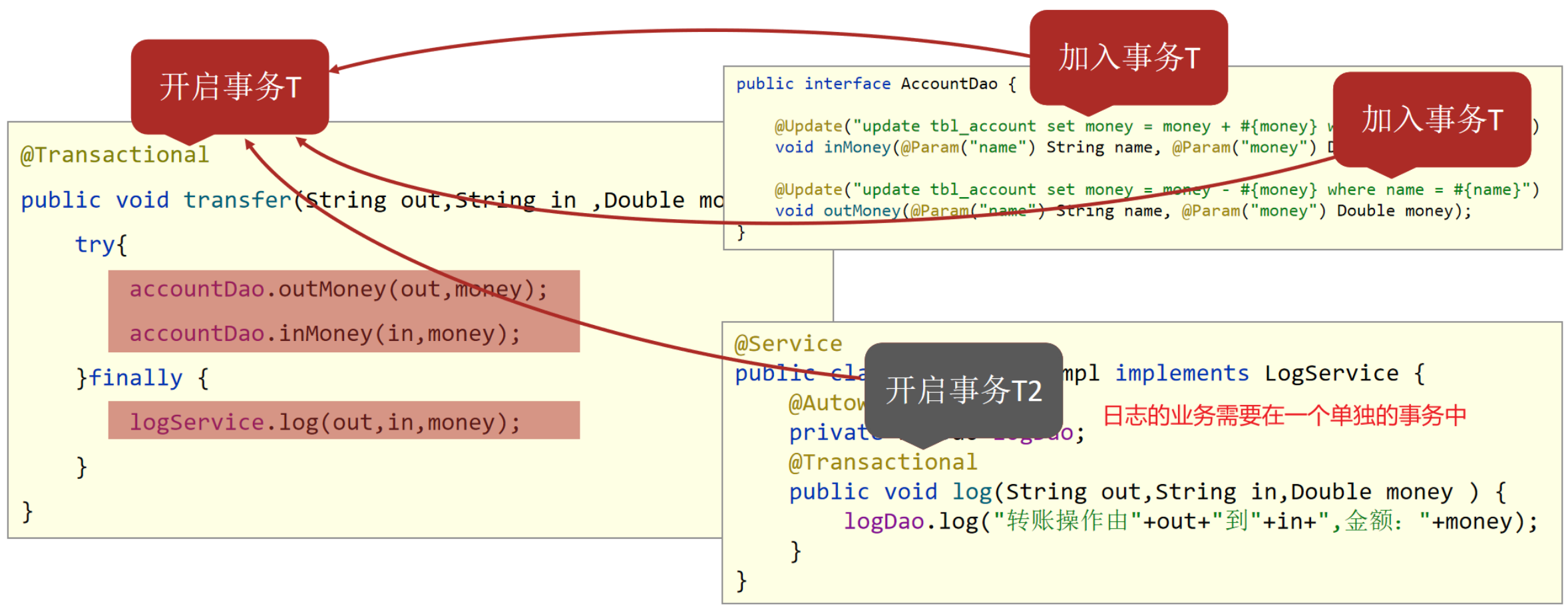
# 2、案例
- 需求:实现任意两个账户间转账操作,并对每次转账操作在数据库进行留痕
spring04_transfer
├── pom.xml
├── src
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── java
│ │ │ └── org
│ │ │ └── example
│ │ │ ├── config // 所有的配置类
│ │ │ │ ├── JdbcConfig.java
│ │ │ │ ├── MybatisConfig.java
│ │ │ │ └── SpringConfig.java // Spring框架的相关内容
│ │ │ ├── dao // 数据访问对象(DAO)
│ │ │ │ ├── AccountDao.java
│ │ │ │ └── LogDao.java
│ │ │ ├── domain // 所有的领域模型类
│ │ │ │ └── Account.java
│ │ │ └── service // 所有的服务类
│ │ │ ├── AccountService.java
│ │ │ ├── LogService.java
│ │ │ └── impl
│ │ │ ├── AccountServiceImpl.java
│ │ │ └── LogServiceImpl.java
│ │ └── resources // 所有的资源文件
│ │ └── jdbc.properties
│ └── test
│ └── java
│ └── AccountServiceTest.java // 测试入口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 1、pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# 2、资源和配置
1)resources/jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db?useSSL=false
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
2)config/SpringConfig.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class,MybatisConfig.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringConfig {
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
3)config/MybatisConfig.java
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("org.example.domain");
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ssfb;
}
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer(){
MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
msc.setBasePackage("org.example.dao");
return msc;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
4)config/JdbcConfig.java
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public class JdbcConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(userName);
ds.setPassword(password);
return ds;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager ptm = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
ptm.setDataSource(dataSource);
return ptm;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
# 3、dao
1)dao/AccountDao.java
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
public interface AccountDao {
// 当调用inMoney方法时,会执行SQL语句update tbl_account set money = money + ? where name = ?
// 其中第一个问号会被参数money的值替换,第二个问号会被参数name的值替换
@Update("update tbl_account set money = money + #{money} where name = #{name}")
void inMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);
@Update("update tbl_account set money = money - #{money} where name = #{name}")
void outMoney(@Param("name") String name, @Param("money") Double money);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2)dao/LogDao.java
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface LogDao {
@Insert("insert into tbl_log (info,createDate) values(#{info},now())")
void log(String info);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 4、domain未使用
# 5、service
1)接口@Transactional- 这是Spring框架中的一个注解,表示这个方法需要进行事务管理
- 如果这个方法在执行过程中出现异常,那么这个方法所做的所有数据库操作都会被回滚
@Transactional(rollbackFor = IOException.class):- 表示如果这个方法抛出IOException异常,那么这个方法所做的所有数据库操作都会被回滚
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)REQUIRES_NEW- 在方法执行期间开启一个新的事务,即使当前已经存在一个事务,新事务也会被创建
- 这个新事务与当前事务无关,它们是两个独立的事务,互相不会影响(保证log日志写入表中)
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新事务;否则加入当前事务SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,则不使用事务MANDATORY:使用当前事务,如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常
// service/AccountService.java
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface AccountService {
//@Transactional(rollbackFor = IOException.class)
@Transactional
public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) throws IOException;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// service/LogService.java
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
public interface LogService {
//propagation设置事务属性:传播行为设置为当前操作需要新事务
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
void log(String out, String in, Double money);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2)类
// service/impl/AccountServiceImpl.java
import org.example.dao.AccountDao;
import org.example.service.AccountService;
import org.example.service.LogService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Autowired
private LogService logService;
public void transfer(String out,String in ,Double money) {
try{
accountDao.outMoney(out,money);
// int i = 1/0;
accountDao.inMoney(in,money);
}finally {
logService.log(out,in,money);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// service/impl/LogServiceImpl.java
import org.example.dao.LogDao;
import org.example.service.LogService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class LogServiceImpl implements LogService {
@Autowired
private LogDao logDao;
public void log(String out,String in,Double money ) {
logDao.log("转账操作由"+out+"到"+in+",金额:"+money);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 6、test入口
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)- 指定了
SpringJUnit4ClassRunner作为测试运行器 - 它能够为测试提供Spring测试上下文(ApplicationContext)
- 这意味着Spring容器会在测试开始前初始化并且在测试结束后关闭
- 指定了
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)- 告诉Spring测试框架使用
SpringConfig.class作为配置信息来创建Spring上下文 SpringConfig.class中定义了Spring容器如何装配bean
- 告诉Spring测试框架使用
import org.example.config.SpringConfig;
import org.example.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Test
public void testTransfer() throws IOException {
accountService.transfer("Tom","Jerry",50D);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
上次更新: 2024/5/31 11:18:42
